In the world of machinery and automation, linear guides are the unsung heroes, quietly ensuring everything runs smoothly. Imagine a rollercoaster ride without tracks—chaotic, right? Linear guides provide that essential path, allowing components to glide with precision and ease. They’re the secret sauce behind everything from 3D printers to CNC machines, making sure parts move like a well-choreographed dance.
Linear Guides
Linear guides play a pivotal role in ensuring smooth and precise movement in various machinery and automation systems. These components significantly enhance the performance and accuracy of mechanical operations.
Definition and Purpose
Linear guides consist of a rolling element system that supports linear motion along a predictable path. Their primary purpose involves reducing friction and improving movement efficiency within machinery. Applications in CNC machines and 3D printers exemplify their importance, as they facilitate high-precision machining and additive manufacturing. Engineers often specify linear guides based on load capacities, size, and intended application to meet specific operational requirements.
Common Applications
Numerous industries rely on linear guides for their efficiency and reliability. CNC machining utilizes linear guides for precise cutting, enhancing overall production quality. Robotics employs these components to ensure accurate and repeatable movements, crucial for automation tasks. In the medical field, linear guides support equipment like surgical robots, improving operational precision and safety. Additionally, packaging machinery benefits from linear guides by ensuring reliable placement and movement of products during the packing process.
Types of Linear Guides
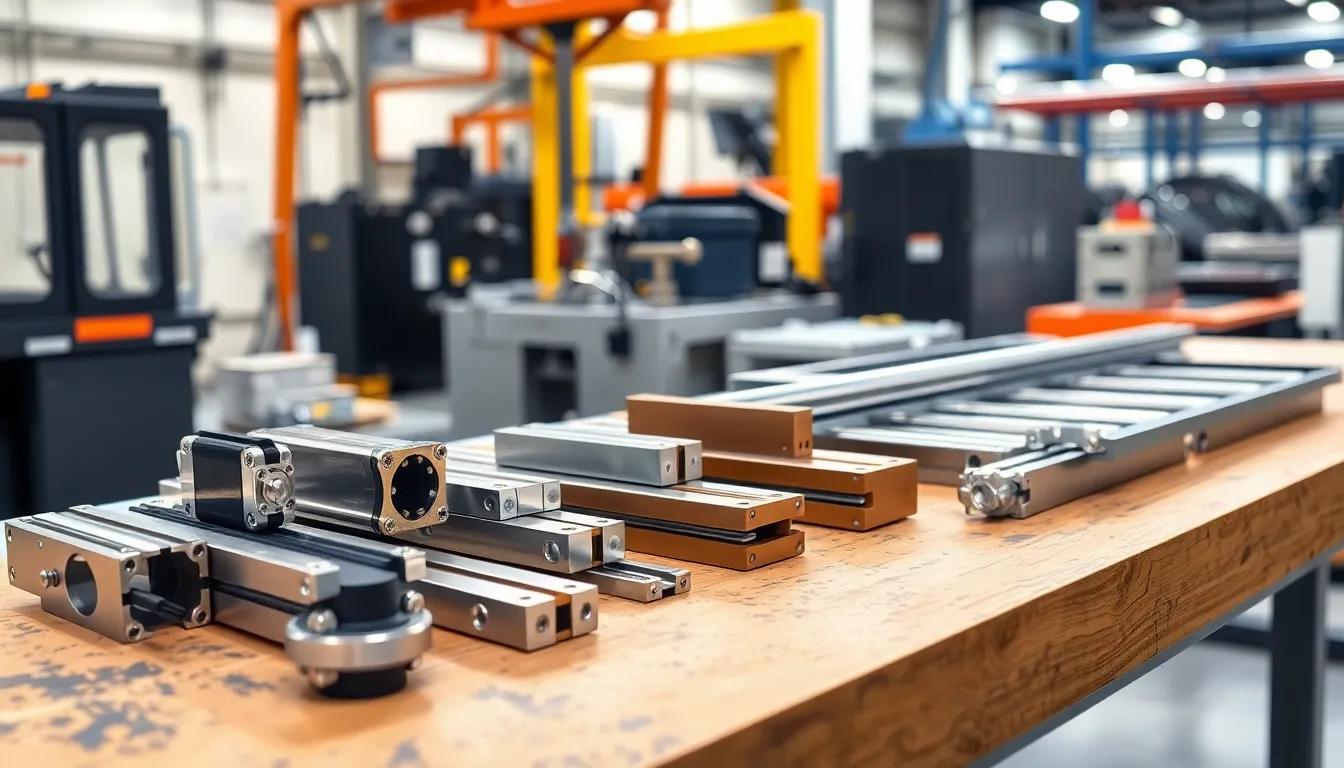
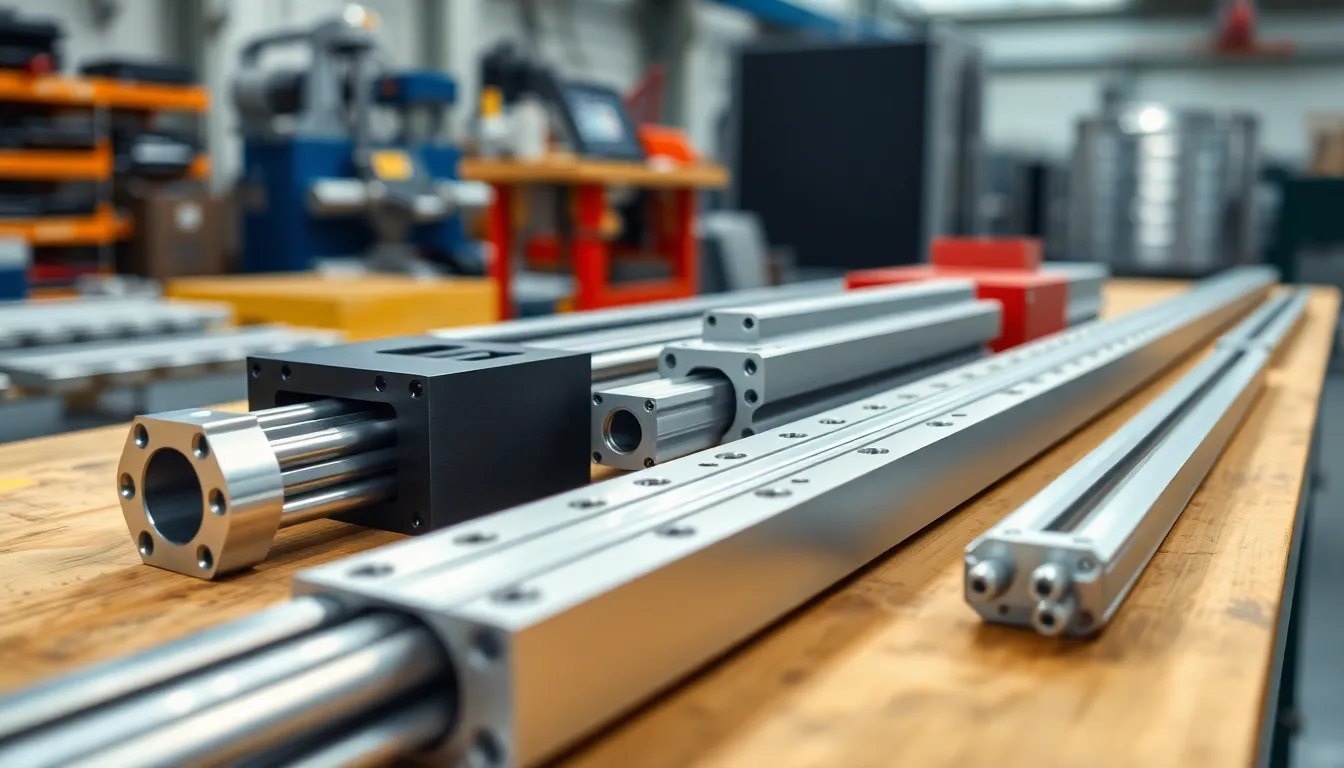


Linear guides come in several types, each tailored for specific applications and performance requirements. Understanding these types helps select the best option for any project.
Ball Rail Guides
Ball rail guides utilize ball bearings to facilitate smooth linear motion. These systems feature a block that rides on a rail, providing low friction and high load capacity. Commonly used in CNC machines, they enable precise and rapid movements. Their design allows for customizable lengths and configurations, making them versatile in various settings. Ball rail guides excel in applications requiring high accuracy, such as robotic automation and medical devices.
Roller Guides
Roller guides employ cylindrical rollers to achieve linear motion with greater load support. Unlike ball rail guides, these systems distribute loads across a larger surface area, enhancing stability. Used frequently in heavy machinery, roller guides perform well under high load conditions. Their construction minimizes wear and extends service life, making them ideal for demanding applications. Industries such as manufacturing and packaging benefit significantly from roller guides’ reliability and durability.
Magnetic Guides
Magnetic guides provide a non-contact solution for linear movement using magnetic forces. These systems offer unique advantages, such as eliminating friction and wear associated with traditional guides. Magnetic guides excel in cleanroom environments or situations where precision is vital. Their ability to maintain smooth motion without physical contact allows for silent operation. Common applications include semiconductor manufacturing and high-speed assembly lines, showcasing their effectiveness in niche industries.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Linear Guides
Selecting the right linear guides hinges on several critical factors. Considering load capacity, speed and accuracy, and environmental durability significantly enhances performance.
Load Capacity
Load capacity plays a pivotal role in selecting linear guides. Different guides support varying weight limits, essential for ensuring reliable operation. Analyzing the maximum load the assembly will experience determines the appropriate size and type of guide necessary for optimal performance. Ball rail guides typically accommodate lighter loads but excel in precision. In contrast, roller guides handle heavier loads, offering superior stability. Evaluating specific application needs helps in choosing suitable linear guides that meet required strength and support demands.
Speed and Accuracy
Speed and accuracy influence the effectiveness of linear guides in various applications. High-speed operations benefit significantly from linear guides designed for rapid movement, while precision applications require guides that maintain dimensional accuracy. Consequently, manufacturers often prioritize the design of guides to minimize friction and enhance motion smoothness. Understanding the operational speeds and required tolerances helps in making informed choices about the most suitable guide types. Incorporating ball rail guides achieves higher speeds, whereas roller guides often offer enhanced durability with slightly lower speeds.
Environment and Durability
Environmental conditions and durability are vital considerations when selecting linear guides. Applications in harsh environments demand guides that resist wear and corrosion. Certain materials, such as stainless steel and special coatings, provide necessary longevity and protection. Additionally, cleanroom environments benefit from non-contact magnetic guides that eliminate dust accumulation and wear. Evaluating temperature ranges, humidity levels, and exposure to chemicals can guide users to select linear guides that ensure long-lasting performance. Prioritizing durability not only enhances the efficiency of equipment but also reduces maintenance and replacement costs.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Proper installation and routine maintenance of linear guides ensure optimal performance and longevity. Following specific steps leads to efficient operation while minimizing unexpected downtime.
Installation Guidelines
Ensure the mounting surfaces are clean and free of debris before installation. Select a level and stable base for precise alignment of the guides. Use manufacturer’s specifications for torque settings when securing the linear guides to maintain proper tension. Employ appropriate tools for installation, as inadequate equipment can lead to misalignment and uneven wear. Verify that the carriage moves smoothly along the guide after installation to confirm correct setup.
Maintenance Practices
Regularly inspect linear guides for signs of wear or damage, focusing on rolling elements and rail surfaces. Lubricate the guides according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, using suitable lubricants for the specific application environment. Keep the guides free from contaminants like dust and moisture to prolong lifespan and efficiency. Replace worn components immediately to avoid potential breakdowns and ensure consistent accuracy in operations. Document all maintenance activities for reference and to track performance over time.